EPIC 'Blank Sky' - XMM-Newton
XMM-Newton EPIC 'Blank Sky' Background
This page concerns the XMM-Newton Blank Sky files and related software available for use with XMM-Newton EPIC data.
Blank sky files were constructed using a superposition of pointed observations that have been processed with SAS version 9.0.0.
Please refer to the paper by Carter and Read (A&A 464, p1155, 2007) for further information on the creation of these files.
Contents:
- Latest updates to these web pages
- XMM-Newton Blank Sky event files
- Creation of the Blank Sky files
- Unfilled and ghosted Blank Sky files
- Watchouts
- Threads
- Software
- Blank Sky file properties
- Link to pre October 2008 Blank Sky page
Latest Updates
- Sep-2013: discontinuation of the tailored blank field event list service
- Aug-2011: Modified skycast script available
- Aug-2010: Blank sky files constructed using observations processed using SAS 9.0.0, up to revolution 1789
- Oct-2008: Major reworking of website to incoporate new file delivery system
XMM-Newton Blank Sky event files
This page was produced as a result of work within the XMM-Newton EPIC Background Working Group.
When performing detailed XMM-Newton EPIC analysis, a good knowledge of the background is required. Sometimes it may be possible to extract the background from a region close to the particular source one is interested in (using a so-called 'local' background). For a large or extended source however, one may have to extract the background far from the target source (the source may in fact be so extended, that no local background is visible within the field of view). Here, a number of effects can cause the extracted local (off-axis) background to be highly inappropriate in analysing the (normally on-axis located) target source, such as the effective area of the mirrors with off-axis angle, instrumental fluorescence and the spectral response which can depend on the position on the detector. These off-axis effects are corrected in the XMM-Newton EPIC calibration.
The files available via these pages are intended to be used in case of difficulty extracting a suitable background region from a user's observation. A guide to these files and their use can be found below.
The creation of individually tailored blank sky files, previously offered by the X-ray and Observational Astronomy Group of the University of Leicester, UK, is now no longer possible. You may find that a blank sky file has already been created that is suitable for your use. Please see the list of selection criteria used in previous submissions in this table. These files have been provided by Jenny A. Carter (Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Leicester, Leicester).
Creation of the Blank Sky files
The component Blank Sky files that make up the final superimposed Blank Sky files were created from event files processed using SAS 9.0.0. Each individual component file that becomes part of a specific instrument-filter-mode set has undergone source removal and flare-screening. The source removal extraction radius is based on the resolved point source flux. A source extraction radius of 45 arcseconds was used for sources with a 2XMM PPS source list EPIC flux above a threshold of 6.0e-13 ergs cm-2 s-1 and 35 arcseconds for below this threshold. We have also implemented an improved removal of known bad pixels for the EPIC-pn. The flare screening is based on the 2XMM PPS background time series files. For MOS they are created for full-field events above 14 keV, and with the selection expression (PATTERN==0) && #XMMEA_22 && ((FLAG & 0x762ba000) == 0), whereas for PN, they are created for full-field, bright-source-excluded all-pattern events between 7 keV and 15 keV. The flare removal that has been used here in the creation of the Blank Sky files (thresholds: 2 counts/s for MOS and 60 counts/s for PN) was based on the very conservative limits suggested by the EPIC instrument teams. A user may therefore wish to undertake some additional flare screening steps when using these files.
The blank sky event lists were generated with the SAS version made public in 2009. Since then, several changes have been introduced in the MOS data reduction pipeline, as well as in the camera calibration. However, these changes are expected to have a minimum impact on the scientific quality of the blank field event lists. The main limiting factor is the accuracy of the energy scale. Strong instrumental lines in the background can yield significant residuals in the background-subtracted spectrum if calibrated at the wrong energy (or if the energy scale of the source plus background spectrum is inaccurately calibrated). However, reduction with SASv9.0 and associated calibration files already achieved a nominal accuracy of the energy scale over the whole detector field-of-view (XMM-CCF-REL-225). Still, we recommend users to exercise astrophysical common sense when interpreting features in blank field background-subtracted spectra close to strong background lines (see, e.g., the discussion in Sect. 8 of the ESAS Cookbook).
Unfilled and ghosted Blank Sky files
There are two types of background event file; unfilled and ghosted. The unfilled event files result from the stacking of event files that have been subjected to various filtering steps, which includes the removal of sources. Therefore proper consideration of the exposure maps is required when using the final event file that applies to a set of combined observations. However, we have developed a method to fill in the source regions that are extracted from each individual observation by sampling events close to the extracted regions and filling the vacated region of the event file, randomising just the spatial coordinates. Adjustments are made for region crossovers and chips edges. This results in smooth (ghosted) event file images and exposure maps. Both types of event file are available here, with corresponding vignetted and non-vignetted exposure maps.
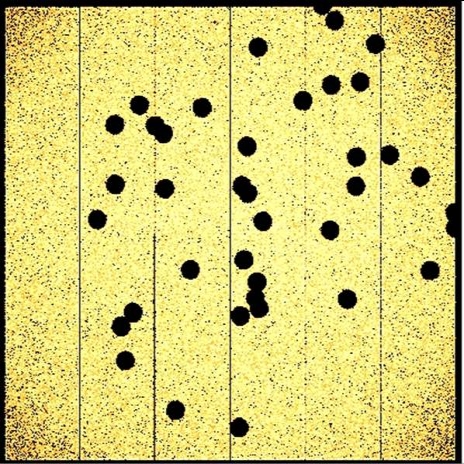 |
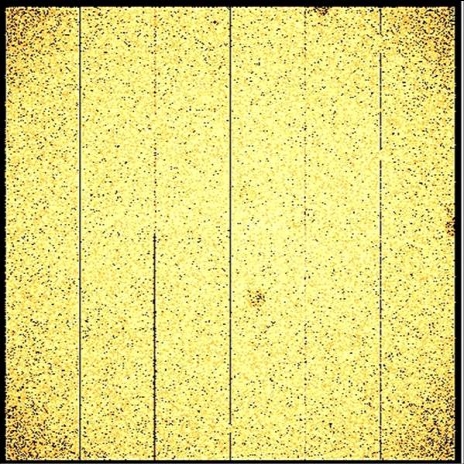 |
| On the left is shown an image created from a pn events file with sources removed, and on the right, the image of the events file after the event filling procedure | |
Watchouts
General watchouts:
- The creation of individually tailored blank sky files has been discontinued. You can find a list of blank sky event lists for a certain combination of sky coordinates, Galactic column density and instrumental configurations here.
- Each Blank Sky file was constructed from several different event files, spanning a large range in time over the mission. Date-related and positional-related keywords, for example DATE-OBS, have therefore been removed. A few SAS tasks require date and time stamp keywords. It is recommended that these keywords be added by the user as required. Missing date and time keywords could be e.g. set to that of the user's source spectrum. This can be achieved for example using the FTOOLS viewer/editor fv:.
- fparkey '2004-07-12T12:30:00.0' blank_sky_event_lists.ds+0 DATE-OBS add=yes
- fparkey '2004-07-12T12:30:00.0' blank_sky_event_lists.ds+1 DATE-OBS add=yes
Users should be aware of a few issues when using ghosted Blank Sky files:
- Due to the method of creation of the ghosted blank sky files, some events with particular flags may be positioned within inappropriate areas of an image, e.g. near a chip gap.
Threads
- How to use EPIC background blank field files.
This thread briefly explains how to make use of blank sky event lists to create background spectra. - Scaling of Blank Sky exposure maps.
The Blank Sky exposure maps were created in the energy range 200 eV to 10000 eV. However, a user may wish to work in a different energy range. We can recommend the following method to scale the Blank Sky exposure maps for use in any required energy range:- From the user's dataset create an exposure map in the required band and also create a similar exposure map in the Blank Sky band with pimin set to 200 and pimax set to 10000.
- Next, calculate the ratio map from these two maps (using, for example the FTOOLS task farith), i.e. divide the exposure map in required band by the exposure map in the original 200 - 10000 eV band. It is recommended that you pre-add (FTOOLS, fcarith) a tiny value, e.g. 1e-20, to the 200-10000 eV map to avoid division by zeros.
- Multiply the Blank Sky exposure map by this ratio map to scale the appropriate Blank Sky exposure map to the required energy range.
Software
All related software can be obtained from here.
Skycast
Script to cast an XMM-Newton EPIC background dataset (or indeed any EPIC event dataset) onto the sky, at the position given by an input template event dataset (e.g. the event file you are interested in producing a background for).
BGrebinimage2SKY
Projection of Sky maps: A script to rebin and reproject exposure maps (or any DETX/DETY image of any binning) onto the sky to the spatial scale and sky position of a user-input image. This is useful when wanting to work in sky coordinates and to a different spatial scale than e.g. the 4 arcsecond scale used in the production of the exposure maps. This script is a wrapper for a fortran executable and is dependent on the user's operating system.
ghostholes_ind
A script that calls the IDL procedure ghostit_ind.pro to fill in the regions that are extracted from each individual observation (e.g. after using the SAS task regions), by sampling events close to the extracted regions and filling the vacated region of the event file, randomising just the spatial coordinates as used in the creation of the Blank Sky ghosted event files. Both the script ghostholes_ind and the IDL procedure ghostit_ind.pro must be downloaded. An EPIC source list file, as created by the SAS task regions and a calibration index file are required to use this script.
Blank Sky file properties
Various properties of the Blank Sky files are described on the web page relating to files prior to October 2008, which can be found here.
Link to pre October 2008 Blank Sky page
The previous page, including access to the old Blank Sky files can be found here.
- Removed a total of (1) style text-align:center;
- Removed a total of (1) align=center.








































 Sign in
Sign in
 Science & Technology
Science & Technology