IoW_20220511 - Gaia
Image of the Week
Systemic proper motions of 73 galaxies in the Local group
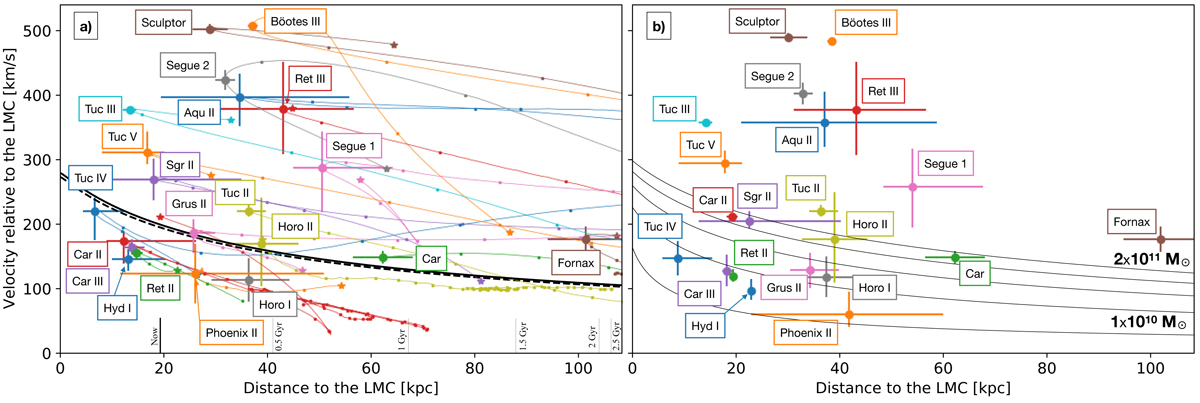
Distance and velocity relative to the LMC for the galaxies that might have passed within 60 kpc from the LMC. Left: Result for a gravitational potential of the Milky Way perturbed by the passage of the LMC. The black lines (both solid and dashed) represent the escape velocity of the initial LMC prior to its accretion by the Milky Way (solid line: LMC = 1.5 x 1011 solar masses / scale radius of 10.84 kpc) and of the current LMC (dashed line). The coloured lines show the past location and velocities of the galaxies, with each dot marking a step of 100 Myr. The galaxies with velocity below the black lines and distance within the Jacobi radius (vertical lines) represent galaxies which were gravitationally bound by the LMC at that given time. Right panel: same but for a Milky Way gravitational potential model where the LMC follows the orbit of a point mass and the Milky Way does not respond to the perturbation of the LMC; the black lines represent the escape velocity of the LMC with a mass for the LMC of respectively 1, 5, 10, 15 and 20 x 1010 solar masses and scale radius following the requirement of Vasiliev et al. (2021). Image credit: G. Thomas (Battaglia G., et al. A&A 2022).
To gain insight in the interactions between our Milky Way and its neighbouring galaxies, knowledge of their position and motion is essential. Using astrometry and photometry from Gaia's Early Data Release 3, a team of scientists from the Instituto de Astrofisica de Canarias in Spain, led by G. Battaglia, have determined the systemic proper motions (so its joint motion as a system) of the largest sample of Local Group galaxies to date. A reliable estimate is in place for 66 systems, and a first estimate for the other 7 galaxies making a total of 73. The results are described in the paper "Gaia Early DR3 systemic proper motions of Local Group dwarf galaxies and orbital properties with a massive Large Magellanic Cloud" by Battaglia, et al. 2022.
The Local Group is the group of galaxies, bound together by their mutual gravitational attraction, where our Milky Way resides and which moves through space as one entity of about 10 million light-years wide (which equals roughly 3 Mpc). Within the group, the motion of these galaxies with respect to one another and especially with respect to the large Local Group spirals are of interest; for example, knowledge of past motions can explain us more about the history of our Milky Way and the interactions that might have shaped the tiny systems that surround it.
Before Gaia's data release 2, when astronomers discussed the systemic proper motions in the Local Group, they were limited to the Magellanic Clouds, M31, M33 and a few other galaxies in our local neighbourhood. With the arrival of precise positions and proper motions in April 2018, the knowledge of the motion of galaxies themselves was extended to about 58 Milky Way satellites. The precision of the proper motion measurements again increased, with a factor 2, in December 2020 when Gaia's early data release 3 was published. This additional step in precision, allowed to push further out and compute the systemic proper motions for 73 galaxies out to an impressively large distance of about 1.4 Mpc. This is now the largest set of systemic proper motions for (candidate) galaxies.
For the galaxies within about 500 kpc from the Milky Way, also the orbital properties were inferred. The approach used was to assume different gravitational potentials for the Milky Way, but this time not only axisymmetric and static gravitational potentials but also one that is triaxial and time-varying. The latter includes the perturbation due to the infall of the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC), assumed to have a mass of 1.5 x 1011 solar masses, and the response of the Milky Way to this perturbation. The Large Magellanic Cloud's dark matter halo could be as large as one tenth to one fifth of that of the Milky Way, hence the importance to take into account the interactions between the LMC and the Milky Way when computing their combined gravitational effect.
The resulting orbital parameters of the galaxies are clearly affected by the infall of the LMC into the Milky Way. The changes range from increased or decreased pericentres/apocentres of the orbits of the Milky Way satellites and their timing and frequency, and occur also for galaxies that are unlikely to have been associated to the LMC. In some cases, the change can be as dramatic as implying a recent infall onto the Milky Way for galaxies that would otherwise have been considered as possible long term companions of our galaxy. Following the assumption of this time-varying Milky Way potential, more results can be deduced. From the figure shown above it can be seen that taking into account the perturbation of the LMC onto the MW leads to different results. For example Carina II is clearly linked to the LMC from the panel on the left, while from the panel on the right, assuming a similar mass for the LMC of 1.5 1011 solar masses, the galaxy Carina II would not be associated to the LMC at all.
More results deduced are that six systems are highly likely to have been satellites of the LMC, three might have potentially been associated to it and one that seems to have been recently captured. The improved astrometry in Gaia EDR3, in the context of the perturbed potential, makes it quite unlikely now that one of the largest Milky Way dwarf galaxies, Fornax, was associated with the LMC.
Exciting times for astronomers digging through Gaia's data. The improved astrometry and photometry data released with Gaia's Early Data Release 3 continues to improve our knowledge of the Milky Way and its surroundings.
Further reading:
- 13/11/2018: Gaia catches the movement of the tiny galaxies surrounding the Milky Way
- 25/04/2018: Gaia’s globular clusters and dwarf galaxies – with orbits
- Paper: "Gaia Early DR3 systemic proper motions of Local Group dwarf galaxies and orbital properties with a massive Large Magellanic Cloud" by Battaglia, et al. 2022.
Credits: ESA/Gaia/DPAC; Battaglia G.
[Published: 11/05/2022]
- Removed a total of (5) style text-align:center;
- Removed a total of (1) style text-align:justify;
Image of the Week Archive
- Removed a total of (1) border attribute.
- Removed a total of (1) cellpadding attribute.
- Removed a total of (1) cellspacing attribute.








































 Sign in
Sign in
 Science & Technology
Science & Technology